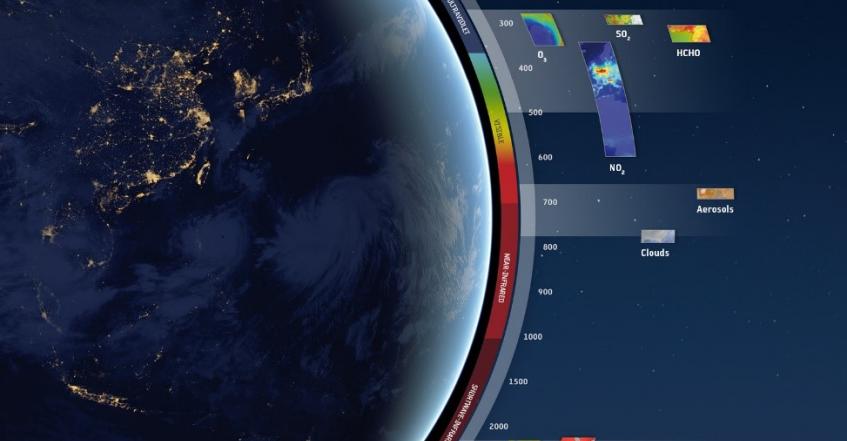
Tropomi - A Powerful Method of Measuring Emissions from Space
Measuring air quality and atmospheric gases with satellites makes it easy to spot and map emissions and pollution around the world. The TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (Tropomi) monitors pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide, ozone, formaldehyde, sulphur dioxide, methane and carbon monoxide. It detects sunlight that has been scattered back into space by the Earth’s surface and atmosphere, analysing the unique fingerprints of gases across different bands of the spectrum.
The Tropomi instrument sits on board the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite and takes measurements every second, covering an area 7km long and 2,600km wide at a resolution of 7km2. This enables it to detect the air pollution profile of individual cities.

Tropomi’s daily global observations are used to improve air quality forecasts and to monitor the concentrations of atmospheric particles. By monitoring trends over time, researchers and regulators can check whether emissions policies are being followed. Additionally, Tropomi contributes to volcanic ash monitoring for aviation safety, warnings for high levels of cancerous UV radiation, and weather predictions.
With its global coverage and free & open data policy, the Tropomi instrument supports international efforts to monitor pollution and to improve our understanding of chemical and physical atmospheric processes. SCARBO is developing technology to complement that effort by measuring carbon dioxide (CO2), another major contributor to climate change.
Learn more at http://www.tropomi.eu


