SCARBO Featured in nature - International Journal of Science
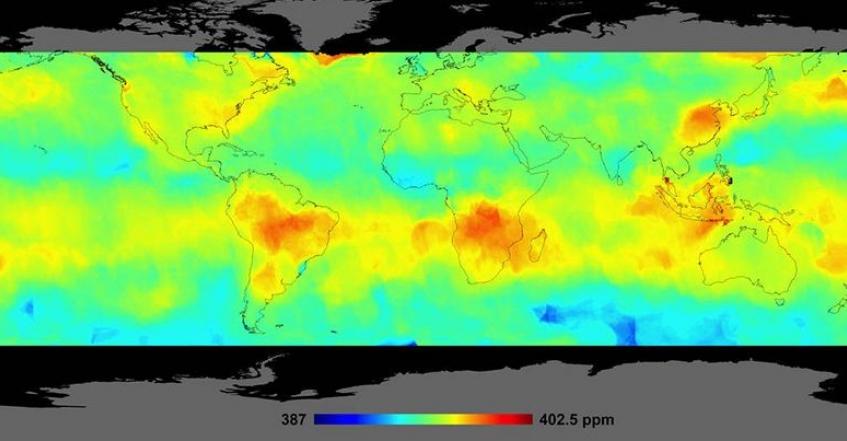
SCARBO was recently featured in an article on nature.com, providing an excellent overview of the project. The article highlights how SCARBO originated from the European Commission’s desire to develop satellite-borne instruments that would measure anthropogenic CO2 emissions and thus enable to assess how whether nations were abiding by their climate change pledges.
The article also discusses the synergies of the project with existing services such as the Copernicus Sentinels, Japan’s GOSAT, the US Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) and China’s TanSat. There are complimentary features between these programmes and SCARBO, however, SCARBO has the specific goal of developing space technologies for tracking international compliance with global treaties.
The challenge facing SCARBO is highlighted within the article and well described. The miniaturisation of technologies such as the spectrometer presents a technological challenge, requiring scientists to demonstrate that the miniaturised systems can deliver sufficient accuracy. SCARBO is aiming to achieve measurements of CO2 concentrations to an accuracy of less than 1 part per million with a spatial resolution of 2 kilometres.
SCARBO plans to test the proposed instrumentation aboard a research airplane in 2020. The plane shall also be equipped with instrumentation for the measurement of atmospheric aerosols, which are a common cause of error in greenhouse gas measurements. This will be the first time that aerosols and carbon dioxide are measured simultaneously to improve the quality of data on greenhouse gas emissions.
For additional details, check out the full article here: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-018-06963-4


